Downtips gives you the best way How to download Revit Software. Here are some instructions and descriptions are given below. We will describe some Points.
- What is Revit software?
- Uses of Revit Software
- Benefits of Revit Software
- How to get Revit Software?
- Errors in Revit Software
What is Revit software?
Revit is a building information modeling (BIM) software developed by Autodesk. It is primarily used by architects, engineers, designers, and building professionals to design, visualize, simulate, and collaborate on building projects from conception through construction. Here’s an overview of what Revit software offers:
- BIM Platform: Revit is built on the concept of BIM, which allows users to create intelligent 3D models of buildings and infrastructure. Unlike traditional 2D drafting software, Revit models contain parametric data that represent real-world building elements such as walls, doors, windows, roofs, and structural components.
- Design and Documentation: Revit enables users to create detailed building designs and generate construction documentation directly from the model. Users can easily design and modify building components, apply materials and finishes, and annotate the model with dimensions, notes, and other information.
- Collaboration: Revit supports collaborative workflows, allowing multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. Changes made by one team member are automatically synchronized with the central model, ensuring everyone is working with the most up-to-date information. Collaboration features include model linking, work sharing, and cloud-based collaboration tools.
- Visualization and Rendering: Revit includes visualization tools that allow users to create photorealistic renderings and visualizations of their designs. Users can apply materials, lighting, and camera views to create compelling visual representations of building projects for presentations and client communication.
- Analysis and Simulation: Revit offers analysis and simulation capabilities to evaluate various aspects of building performance, such as energy efficiency, structural integrity, and lighting levels. Users can perform energy analysis, structural analysis, lighting analysis, and more directly within the software to optimize building designs and meet performance goals.
- Interoperability: Revit supports interoperability with other Autodesk software as well as industry-standard file formats. Users can import and export models, drawings, and data between Revit and other software applications such as AutoCAD, Navisworks, and various engineering analysis tools.
- Customization and Extensions: Revit can be customized and extended through the use of add-ins, macros, and scripting. Users can develop custom tools and workflows to automate repetitive tasks, enhance productivity, and tailor the software to their specific needs.
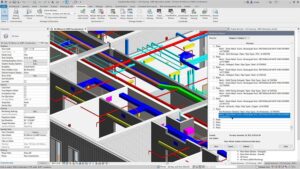
Uses of Revit Software:
Revit software is widely used across the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries for various purposes. Here are some common uses of Revit:
- Architectural Design: Architects use Revit to create detailed architectural designs for buildings and structures. They can design floor plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models of buildings, incorporating elements such as walls, windows, doors, roofs, and stairs.
- Structural Engineering: Structural engineers use Revit to design and analyze the structural components of buildings, such as beams, columns, slabs, and foundations. They can model and simulate the structural behavior of buildings to ensure they meet safety and performance requirements.
- Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Design: MEP engineers use Revit to design the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems of buildings. They can model HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, electrical distribution systems, plumbing fixtures, and fire protection systems, ensuring they are properly integrated with the building design.
- Construction Documentation: Revit is used to generate construction documentation, including drawings, schedules, and specifications, directly from the building model. This streamlines the documentation process and helps ensure accuracy and consistency between design and construction documents.
- Visualization and Rendering: Revit includes visualization tools that allow users to create photorealistic renderings and visualizations of building designs. This helps architects and designers communicate their ideas effectively to clients, stakeholders, and project teams.
- Building Performance Analysis: Revit offers analysis and simulation capabilities to evaluate various aspects of building performance, such as energy efficiency, thermal comfort, daylighting, and structural integrity. This allows designers to optimize building designs and make informed decisions about building materials and systems.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Revit supports collaborative workflows, allowing multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. It also facilitates coordination between different disciplines (e.g., architecture, structure, MEP) by providing tools for model linking, clash detection, and coordination reviews.
- Facility Management: Revit models can be used for facility management purposes, allowing building owners and operators to access information about building components, systems, and maintenance requirements. This helps streamline facility operations and maintenance throughout the building’s lifecycle.
- BIM Coordination and Integration: Revit can be used for BIM coordination and integration with other software tools and platforms. It supports interoperability with various file formats and standards, allowing users to exchange data and collaborate with partners and stakeholders who may use different software tools.
Benefits of Revit Software?
Revit software offers numerous benefits to architects, engineers, designers, contractors, and building owners involved in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Comprehensive Building Information Modeling (BIM) Platform: Revit is a powerful BIM software that allows users to create intelligent 3D models of buildings and infrastructure. These models contain parametric data that represent real-world building elements, enabling users to design, visualize, simulate, and analyze building projects with accuracy and efficiency.
- Improved Collaboration: Revit supports collaborative workflows, allowing multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. Changes made by one team member are automatically synchronized with the central model, ensuring everyone is working with the most up-to-date information. This facilitates better coordination between architects, engineers, contractors, and other project stakeholders.
- Efficient Design and Documentation: Revit streamlines the design and documentation process by allowing users to generate construction documentation directly from the building model. Users can easily create detailed drawings, schedules, and specifications, reducing the time and effort required to produce accurate and consistent documentation.
- Visualization and Rendering: Revit includes visualization tools that allow users to create photorealistic renderings and visualizations of building designs. This helps architects and designers communicate their ideas effectively to clients, stakeholders, and project teams, enhancing decision-making and project approval processes.
- Building Performance Analysis: Revit offers analysis and simulation capabilities to evaluate various aspects of building performance, such as energy efficiency, thermal comfort, daylighting, and structural integrity. This allows designers to optimize building designs and make informed decisions about building materials and systems, leading to more sustainable and resilient buildings.
- Enhanced Coordination and Clash Detection: Revit facilitates coordination between different disciplines (e.g., architecture, structure, MEP) by providing tools for model linking, clash detection, and coordination reviews. This helps identify and resolve conflicts or discrepancies in the building design before construction begins, reducing costly errors and rework during construction.
- Customization and Extensibility: Revit can be customized and extended through the use of add-ins, macros, and scripting. Users can develop custom tools and workflows to automate repetitive tasks, enhance productivity, and tailor the software to their specific needs, making it adaptable to a wide range of project requirements and workflows.
- Streamlined Facility Management: Revit models can be used for facility management purposes, allowing building owners and operators to access information about building components, systems, and maintenance requirements. This helps streamline facility operations and maintenance throughout the building’s lifecycle, improving efficiency and reducing lifecycle costs.
How to get Revit Software?
To download Revit software, you can follow these general steps:
- Visit Autodesk’s Website: Go to Autodesk’s official website (www.autodesk.com) using your web browser.
- Navigate to Revit Product Page: Once on Autodesk’s website, navigate to the Revit product page. You can usually find it under the “Products” or “Software” section. Alternatively, you can use the search function on the website to search for “Revit.”
- Choose Your Version and Subscription Type: On the Revit product page, you’ll typically see options to choose the version of Revit you want to download (e.g., Revit 2023, Revit 2022, etc.). You may also need to select the type of subscription you prefer, such as a monthly, annual, or multi-year subscription.
- Sign In or Create an Autodesk Account: Before downloading Revit, you’ll need to sign in to your Autodesk account or create a new one if you don’t have an account already. This step may require providing your email address, creating a password, and providing some basic information.
- Select Download Option: Once you’re signed in and have chosen your version and subscription type, you’ll typically see a “Download” or “Get Revit” button. Click on this button to initiate the download process.
- Download and Install Autodesk Desktop App (Optional): In some cases, Autodesk may prompt you to download and install the Autodesk Desktop App, which helps manage your Autodesk software installations and updates. You can choose to download and install this app or proceed with downloading Revit directly.
- Download Revit Installer: After clicking the download button, Revit installer files will begin to download to your computer. The file size can be significant, so it may take some time depending on your internet connection speed.
- Run Revit Installer: Once the download is complete, locate the Revit installer file (usually in your computer’s Downloads folder) and double-click it to run the installer.
- Follow Installation Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions provided by the installer to install Revit on your computer. You may need to agree to the terms of service, choose installation options, and specify the installation directory.
- Activate Revit: After installation, launch Revit and sign in with your Autodesk account credentials to activate your software license. Once activated, you can start using Revit for your design and modeling projects.
Errors in Revit Software:
Like any software, Revit can encounter errors or issues that may impact its performance or functionality. These errors can range from minor glitches to more serious technical issues. Here are some common types of errors that users may encounter in Revit:
- Crashes: Revit may occasionally crash or freeze, causing the software to become unresponsive and requiring the user to restart the program. Crashes can occur due to various factors such as hardware compatibility issues, software conflicts, or memory limitations.
- Model Corruption: Sometimes, Revit models can become corrupted, leading to issues such as missing elements, incorrect geometry, or unexpected behavior. Model corruption can occur due to factors like software bugs, file corruption during saving or transferring, or hardware failures.
- Performance Issues: Revit’s performance may degrade over time, especially with large or complex models. Users may experience slow response times, lagging interactions, or delays in model updates. Performance issues can be caused by factors such as insufficient system resources, outdated hardware, or inefficient model elements.
- Rendering Errors: When generating renderings or visualizations in Revit, users may encounter errors such as artifacts, texture mapping issues, or incorrect lighting effects. Rendering errors can be caused by factors like insufficient hardware resources, software bugs, or improper settings.
- Compatibility Problems: Revit models created in newer versions of the software may not be compatible with older versions, leading to issues when opening or editing the files. Compatibility problems can also arise when importing or exporting models between Revit and other software applications.
- License Activation Issues: Users may encounter difficulties activating their Revit licenses, such as invalid license keys, activation failures, or license server connectivity issues. License activation issues can be caused by factors like incorrect license information, network configuration problems, or server downtime.
- Add-in Compatibility: Third-party add-ins or extensions for Revit may not function properly or may cause conflicts with other software components. Users may experience errors, crashes, or unexpected behavior when using incompatible or outdated add-ins.
- Update and Patch Problems: Installing updates or patches for Revit may sometimes result in errors or issues, such as installation failures, compatibility problems, or unintended changes to software settings. Users should exercise caution when installing updates and ensure that they are compatible with their system configuration.
