Downtips gives you the best way How to solve Network Connectivity Troubleshoot. Here are some instructions and descriptions are given below.
What is Network Connectivity?
Network connectivity refers to the ability of devices, systems, or networks to establish and maintain communication with each other over a network. It encompasses the transmission of data, information, or signals between connected devices, allowing them to share resources, exchange messages, and collaborate effectively.
Network connectivity can occur over various types of networks, including:
- Local Area Networks (LANs): LANs connect devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or campus. They typically use Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi connections to facilitate communication between computers, printers, servers, and other networked devices.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): WANs connect devices across larger geographical distances, often spanning multiple cities, countries, or continents. They rely on telecommunications infrastructure, such as leased lines, fiber-optic cables, and satellite links, to enable long-distance communication between interconnected networks and systems.
- Wireless Networks: Wireless networks use radio frequency signals to transmit data between devices without the need for physical cables. Examples include Wi-Fi networks, which provide wireless internet access to devices within range of a wireless access point (router), and cellular networks, which enable mobile devices to connect to the internet via cellular towers.
- Internet: The Internet is a global network of interconnected networks that allows devices and systems worldwide to communicate and exchange data. It provides a vast array of services and resources, including websites, email, file sharing, streaming media, and online collaboration tools.
Network connectivity enables various applications and services to function seamlessly, including:
- Accessing the internet and browsing websites
- Sending and receiving emails
- Streaming audio and video content
- Conducting video conferencing and online meetings
- Sharing files and documents
- Accessing remote servers and cloud-based services
- Collaborating with colleagues or teammates in real-time
Effective network connectivity relies on robust network infrastructure, including routers, switches, access points, cables, and other networking components, as well as reliable internet connectivity provided by internet service providers (ISPs). When network connectivity is disrupted or impaired, it can lead to communication failures, service interruptions, and productivity losses for individuals and organizations relying on network-dependent services and applications. Therefore, maintaining and troubleshooting network connectivity is essential for ensuring the smooth operation of networked systems and services.
How to solve Network Connectivity Troubleshoot?
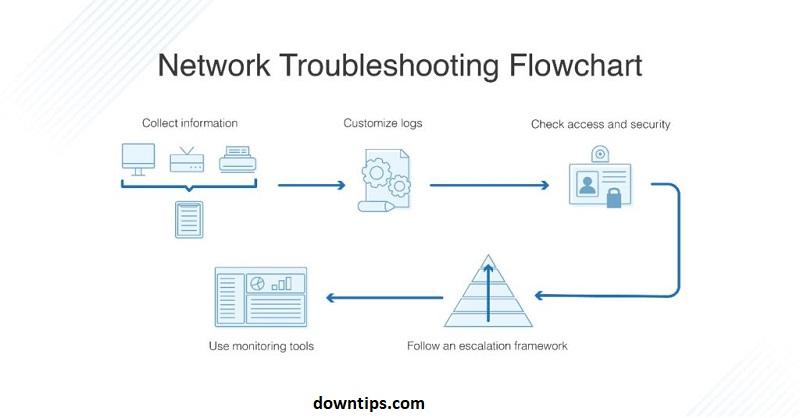
Network connectivity issues can be frustrating, but they can often be resolved by following a systematic troubleshooting process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you diagnose and fix network connectivity problems:
- Check Physical Connections:
- Ensure that all cables, connectors, and devices (such as routers, modems, switches, and computers) are properly connected and powered on. Check for any loose or damaged cables and reconnect them if necessary.
- Restart Devices:
- Sometimes, simply restarting your network devices can resolve connectivity issues. Turn off your modem, router, and computer, then wait a few minutes before turning them back on in the following order: modem → router → computer.
- Verify Internet Connection:
- Confirm whether your internet connection is working by trying to access websites or online services from a different device connected to the same network. If other devices can connect to the internet, the problem may be isolated to your computer or device.
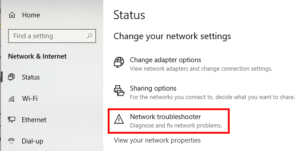
- Check Network Settings:
- Review your network settings on your computer or device to ensure they are configured correctly. Check for issues such as incorrect IP address settings, DNS configuration, or network adapter settings. You can usually find network settings in the Control Panel or System Preferences of your operating system.
- Reset Network Settings:
- Resetting network settings on your computer or device can sometimes resolve connectivity issues. You can try resetting network settings to their default values or using built-in troubleshooting tools provided by your operating system.
- Run Network Diagnostics:
- Use network diagnostic tools provided by your operating system or network hardware to identify and diagnose connectivity problems. These tools can help pinpoint issues such as connectivity errors, DNS resolution problems, or network configuration issues.
- Check Firewall and Security Software:
- Verify that your firewall and security software settings are not blocking network connections or interfering with network traffic. Temporarily disable the firewall or security software to see if it resolves the issue, but remember to re-enable it afterward for security purposes.
- Update Network Drivers:
- Ensure that your network adapter drivers are up to date. Outdated or corrupted network drivers can cause connectivity problems. You can update network drivers manually through Device Manager (Windows) or System Preferences (macOS), or use third-party driver update software.
- Scan for Malware or Viruses:
- Run a full system scan with antivirus or antimalware software to check for any malicious software that may be affecting your network connectivity. Malware or viruses can sometimes interfere with network connections and cause issues.
- Contact Your Internet Service Provider (ISP):
- If you’ve tried all the above steps and are still experiencing network connectivity problems, contact your ISP for further assistance. There may be an outage in your area or an issue with your internet connection that requires intervention from your ISP’s support team.